2 Parallel-Plate Transmission Line (Geometric Model) = c Assume it s a plane wave propagate in the z with polarization in y direction. d dz ~ ˆ.
|
|
|
- Constance Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tansmission ines 1 ntoution When the soue aiates in a ie aea, the eneg speas out. The aiate eneg is not guie an the tansmission of eneg though aiation is ineffiient. Dietive antenna oul have huge imensions in the oe of the ave length of the boaasting eletomagneti aves. We stu the tansvese eletomagneti (TM) aves guie b tansmission lines. The haateistis of TM aves guie b tansmission lines ae the same as those fo a unifom plane ave popagating in an unboune ieleti meium. The thee most ommon tpes of guiing stutues: 1. Paallel-plate tansmission line. At mioave fequenies, paallel-plate tansmission lines an be fabiate on a ieleti substate using pint-iuit tehnolog. The ae often alle stiplines.. To-ie tansmission line: poe an telephone lines. 3. oaial tansmission line: T ables an the input ables to high-fequen peision measuing instuments. Paallel-Plate Tansmission ine (eometi Moel) Phsial Moel 1 i t sine e ω ω + ( + k ) Assume it s a plane ave popagate in the ith polaiation in ietion. + k ik + e 1 1 v (+), ik e + ik +, ( ) e 1 ik+ ω e ( k ω ) v + ik + e (-) When the TM ave popagates in the paallel-plate tansmission line, hage an uent ma be inue in the plates. ossing the bouna fom ieleti meium to the pefet onution plates:, // D // D
2 ++++ at (loe plate) n, D ρ loe plate & n D ik e + e ik+ K J K D K 1 e Use an Ampee s loop to obtain the sufae uent. ik+ at (uppe plate) U ik+ e n & K U 1 e ik+ K n the ieleti meia, the eleti an magneti fiels satisf the Maell s eqs: B & B iω & iω,, (, ) ( basi iffeential equations i j k iω ω ω i & i Use Maell s equation to get the to basi iffeential equations. iω, sine KU D K U
3 K & u iω KU u iω ( K ) iω iω ' is the inutane pe unit length ( ) l l t Use integation to obtain the voltage an uent elation, an to alulate the inutane pe unit length fom ou phsial moel. iω l iω ( ) ( K ) ( ) iω iω iω hee 1 Q 1 l t l t U ( ' ) ' l t iω K U is the apaitane pe unit length Use integation to obtain the apaitane pe unit length. l Time hamoni tansmission line equations: iω & ik e ω & iω ω, ω ω v ω ik + k, ( e, ik ik e, (, e + iω Deive iffeential equation / ik iω iω Use the eive iffeential equations to obtain the uent an voltage vaiation as a funtion of an t. The impeane: ω / k / Z (not ivie b length) The veloit of popagation along the line is:
4 ω v k ( / )( / ) Obtain impeane an spee of popagation aves. Miostip ines The evelopment of soli-state mioave evies an sstems has le to the ie spea use of a fom of paallel-plate tansmission lines alle miostip lines o simpl stiplines. The miostip lines ae lose to the paallel-plate tansmission lines if >>. oss Paallel-Plate Tansmission ines Q D s s l l R l J s l s R et sufae impeane an esistane fom the onept of poe loss. When the apaitane beteen the to onutos, the pemittivit an the onutivit ae kno, e have ( ) 1 Aveage Poe Dissipation: pavg p sufae Re{ } (Ponting s theoem) Uppe plate: K Define a sufae impeane: U Z R + ix Sufae Sufae Sufae Z Sufae K Sufae K S
5 Obtain the sufae impeane fom the onept of attenuate aves in a pefet onuto. A goo onuto is a meium fo hih >> ω. i ( ) ( k +ωt t, e ), + k i ω ω i ω ω ω ω i ω 1 1 ω + i 1 1 k k i ω 1 ω Z R + ix ( 1 i) K ω Sufae Sufae Sufae + U Obtain esistane of a paallel-plate tansmission line. ( + i) RSufae psufae Re{ KU ZSufae} KU RSufeae, P psufae KU RSufae The effetive seies esistane pe unit length fo both plates of a paallel-plate tansmission line of ith is R R ω Sufae (to times fom the viepoint of poe issipation) (pe unit length) l R Z sufae (not ivie b length) K Kl l l
6 3 eneal Tansmission-ine quations (letoni iuit Moel) R Q D s s l l l J s l s R The apaito is the apabilit of stoing hages pe volt. The onuto is the uent flo pe volt. ( in paallel plate tansmission lines) i(, -Q +Q i(, v(, R i(+, v(+, i v R i v, v Ri i + ( + v i v i, i v v + { } ( + { } let ( ) ( ) i ω v, t Re e t an ( ) ( ) i ω i, t Re e t ( R + iω) an ( + iω) let k ( ( R + iω ) ) ( R + iω) ( R + iω)( + iω) e & k k ( R + iω )( + iω) k ( R + iω )( + iω)
7 let k α + iβ ( R + iω)( + iω) i (α : attenuation onstant, β : phase onstan + k + k e + e k + k+ iω t + k+ ( ) ( e + e + k + an e + e ( v + k+ iω t + k+ ( e + e, ), an + k k + k k ( R + iω) k e k e ( R + i )( e + e ) + R + iω k ω haateisti impetane: Z R + iω k R + iω + iω ( / l / l ) (not ivie b length) ample: Demonstate the analog beteen the ave haateistis on a tansmission line an unifom plane aves in a loss meium. n a loss meium, e appl the moel use to esibe fequen epenent pemittivit. The pemittivit is theefoe a omple numbe, ' i ''. The same as pemittivit, e ma have omple pemeabilit, ' i' '. The Maell s equations to elative magneti an eleti fiels ae: iω( ' i '') & iω( ' i '') Assume a unifom plane ave haateie b an that vaies ith onl ith. (Keep in min that a ave funtion popagating in the ietion ith a polaiation in the ietion. The magneti fiel is in the ietion.) ( ' i '') ( ω '' iω ') iω + i j k i i ( ' i '') i ω ( ω '' + iω ') ( ω '' + iω ') ( ω '' + iω ')( ω '' + iω ') k let e & k ( ω '' + iω ')( ω '' + iω ') k & k
8 Deive fom geneal tansmission line equations, e have ( R + iω )( + iω) k. Thee limiting ases: 1. ossless ine ( R,. Thee is no eal pat in k.) (a) Popagation onstant: k iω, α, β ω ω 1 (b) Phase veloit: v phase β () haateisti impeane: X R + iω Z R + ix + iω, R,. o-oss ine ( R << ω, << ω ) (a) Popagation onstant: k iω R + R 1 i 1 i ω ω + iω iω R 1 i i ω ω R α +, β ω ω 1 (b) Phase veloit: v phase β R + iω () haateisti impeane: Z R + ix + iω Z 1/ 1/, R R 1 i 1 i 1 i + i ω ω ω ω R, X ω R ω 1 3. Distotionless ine ( R / / ) R (a) Popagation onstant: k iω 1 i R + iω ω α R, β ω
9 ω 1 (b) Phase veloit: v phase β R + iω R () haateisti impeane: Z R + ix, + iω R, X The iffeent fequen omponents tavel along a tansmission line at the same veloit in oe to avoi istotion. Fo a loss line, ave amplitue ill be attenuate, an istotion ill esult hen iffeent fequen omponents attenuate iffeentl, even hen the tavel ith the same veloit. ample: t is foun that the attenuation on a 5 (Ω) istotionless tansmission line is.1 (B/m). The line has a apaitane of.1 (nf/m). a) Fin the esistane, inutane, an onutane pe mete of the line. b) Fin the veloit of ave popagation. ) Detemine the peentage to hih the amplitue of a voltage taveling ave eease in 1 (km) an in 5 (km). 5 (Ω) eal pat of haateisti impeane 1 nepe eibels R / /.1 3 a) R 5Ω, α R.1( B / m) ( Np / m) ( Np / m) ( F / m) R.5 1 ( / m).5( / m) ( m) 3 R α R / Ω R.8 / ( S m) 1 8 b) v phase 1 m / s α ) Afte 1 (km), / e e α Afte 5 (km), / e e Tansmission-ine Paametes The eletial popeties of a tansmission line ae ompletel haateie b its fou paametes R,,, an.
10 et R k iω ( + iω) iω 1 + iω ompae ith k iω ω k iω 1 + iω 1. To-ie tansmission line. The ies have a aius a an ae sepaate b a istane D. (Obtain the apaitane fom the metho of images.) P Sufae osh 1 π πap ( D / a) Sufae D ( ) osh 1, π a 1 1 RSufae πa K RSufae πa osh 1 π ( D / a) ω RS R (The fato of is not fom seies esistane but fom poe πa πa issipation.). oaial tansmission line. b ln ( ) π a π an ln ( b / a) πa ln ( b / a) 1 RS R πak Si πbk So, PS, i πaps, i & P 1 S S, o πa πb ω RS R + + π a b π a b Attenuation onstant fom Poe Relations The attenuation onstant of a taveling ave on a tansmission line: { } {} k ( R + iω)( iω) α Re Re + Fin the attenuation onstant fom poe elation: k k k e & e e Z The time aveage poe popagate along the tansmission line is: P 1 α Re{ } e Z Time-aveage poe loss pe unit length: P P P
11 P P αp α P P eise: The folloing haateistis have been measue on a loss tansmission line at 1 M: Z 5 + (Ω), α.1 (B/m), β.8p (a/m) i Detemine R,,, an fo the line.
2. Electrostatics. 2.1 What is electrostatics and electrostatic induction? 2.2 Explain coulomb s law of electrostatics
 . Eletostatis. What is eletostatis an eletostati inution? Eletostatis is a banh of siene ealing with eletiity at est i.e. stati eletiity. Nomally evey atom has an ual numbe of potons (ve hage) an eletons
. Eletostatis. What is eletostatis an eletostati inution? Eletostatis is a banh of siene ealing with eletiity at est i.e. stati eletiity. Nomally evey atom has an ual numbe of potons (ve hage) an eletons
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Chapter 1. Vector Calculus. Analysis Basics of Calculus. Derivative. Integral
 : Chapte nalsis Basis of Calulus Veto Calulus http://taps.u.eu.o/phsis/couses/phs/chaptep Deivative The infinitesimal ate of hange in a funtion with espet to one of its paametes. Deivative The eivative
: Chapte nalsis Basis of Calulus Veto Calulus http://taps.u.eu.o/phsis/couses/phs/chaptep Deivative The infinitesimal ate of hange in a funtion with espet to one of its paametes. Deivative The eivative
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
In electrostatics, the electric field E and its sources (charges) are related by Gauss s law: Surface
 Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior P.V.T Relationships for Liquid and Solid:
 hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
Physics 11-0-Formulas - Useful Information. h hc. Earth's mass Earth's radius. Speed of light. Moon's radius. Moon's mass.
 Physis - 0-Fomulas - Useful Infomation unifie atomi mass unit u.66 x 0-7 kg 9 Me V/ Poton mass m p.67 x 0-7 kg Neuton mass m n.67 x 0-7 kg Eleton mass m e 9. x 0 - kg The hage of eleton e.6 x 0-9 C Avogao's
Physis - 0-Fomulas - Useful Infomation unifie atomi mass unit u.66 x 0-7 kg 9 Me V/ Poton mass m p.67 x 0-7 kg Neuton mass m n.67 x 0-7 kg Eleton mass m e 9. x 0 - kg The hage of eleton e.6 x 0-9 C Avogao's
Equilibria of a cylindrical plasma
 // Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
// Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
b) The array factor of a N-element uniform array can be written
 to Eam in Antenna Theo Time: 18 Mach 010, at 8.00 13.00. Location: Polacksbacken, Skivsal You ma bing: Laboato epots, pocket calculato, English ictiona, Råe- Westegen: Beta, Noling-Östeman: Phsics Hanbook,
to Eam in Antenna Theo Time: 18 Mach 010, at 8.00 13.00. Location: Polacksbacken, Skivsal You ma bing: Laboato epots, pocket calculato, English ictiona, Råe- Westegen: Beta, Noling-Östeman: Phsics Hanbook,
ECE Microwave Engineering
 ECE 5317-6351 Mirowave Engineering Aapte from notes by Prof. Jeffery T. Williams Fall 18 Prof. Davi R. Jakson Dept. of ECE Notes 7 Waveguiing Strutures Part : Attenuation ε, µσ, 1 Attenuation on Waveguiing
ECE 5317-6351 Mirowave Engineering Aapte from notes by Prof. Jeffery T. Williams Fall 18 Prof. Davi R. Jakson Dept. of ECE Notes 7 Waveguiing Strutures Part : Attenuation ε, µσ, 1 Attenuation on Waveguiing
E(r,t) = e 3. r 3. (b) Show that the transverse current, J t,is 3n(n e 3 ) e 3
 Polem Set 3 (Jakson 6.20).. An example of the pesevation of ausality and finite speed of popagation in spite of the use of the Coulomg gauge is affoded y a unit stength dipole soue that is flashed on and
Polem Set 3 (Jakson 6.20).. An example of the pesevation of ausality and finite speed of popagation in spite of the use of the Coulomg gauge is affoded y a unit stength dipole soue that is flashed on and
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5
 Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER 2: PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
 EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and close
EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and close
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Electric Anisotropy, Magnetic Anisotropy, Uniaxial and Biaxial Materials, Bianisotropic Media (Definitions)
 leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Supplementary Information for On characterizing protein spatial clusters with correlation approaches
 Supplementay Infomation fo On chaacteizing potein spatial clustes with coelation appoaches A. Shivananan, J. Unnikishnan, A. Raenovic Supplementay Notes Contents Deivation of expessions fo p = a t................................
Supplementay Infomation fo On chaacteizing potein spatial clustes with coelation appoaches A. Shivananan, J. Unnikishnan, A. Raenovic Supplementay Notes Contents Deivation of expessions fo p = a t................................
INFN School on Electron Accelerators. Beam Acceleration Cavity Field and Concepts
 INFN Shool on leton Aeleatos -4 Septembe 7, INFN Sezione di Pisa Letue b Beam Aeleation Cavity Field and Conepts Calo Pagani Univesity of Milano INFN Milano-LASA & GD Linea Collide Coneptual Sheme Final
INFN Shool on leton Aeleatos -4 Septembe 7, INFN Sezione di Pisa Letue b Beam Aeleation Cavity Field and Conepts Calo Pagani Univesity of Milano INFN Milano-LASA & GD Linea Collide Coneptual Sheme Final
not to be republished NCERT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Chapter Eight MCQ I
 Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
An Improved Modeling of TDR Signal Propagation for Measuring Complex Dielectric Permittivity
 Jounal of Eath Siene, ol. 26, No. 6, p. 827 834, Deembe 215 ISSN 1674-487X Pinted in China DOI: 1.17/s12583-15-599-7 An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity
Jounal of Eath Siene, ol. 26, No. 6, p. 827 834, Deembe 215 ISSN 1674-487X Pinted in China DOI: 1.17/s12583-15-599-7 An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity
EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 2: PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
 EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and
EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and
Experiment I Voltage Variation and Control
 ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
Special Relativity in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Waves Without Phase Invariance and Lorentz Transformations 1. Introduction n k.
 Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Physics 2A Chapter 10 - Moment of Inertia Fall 2018
 Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Physics Chapte 0 - oment of netia Fall 08 The moment of inetia of a otating object is a measue of its otational inetia in the same way that the mass of an object is a measue of its inetia fo linea motion.
Fields and Waves I Spring 2005 Homework 8. Due: 3 May 2005
 Fields and Waves I Sping 005 Homewok 8 Tansmission Lines Due: 3 May 005. Multiple Choice (6) a) The SWR (standing wave atio): a) is a measue of the match between the souce impedance and line impedance
Fields and Waves I Sping 005 Homewok 8 Tansmission Lines Due: 3 May 005. Multiple Choice (6) a) The SWR (standing wave atio): a) is a measue of the match between the souce impedance and line impedance
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Errors in Waveguide Samples for the Nicolson-Ross-Weir Permittivity Technique
 Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
PH126 Exam I Solutions
 PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
ELECTROSTATICS::BHSEC MCQ 1. A. B. C. D.
 ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
General Relativity Homework 5
 Geneal Relativity Homewok 5. In the pesence of a cosmological constant, Einstein s Equation is (a) Calculate the gavitational potential point souce with = M 3 (). R µ Rg µ + g µ =GT µ. in the Newtonian
Geneal Relativity Homewok 5. In the pesence of a cosmological constant, Einstein s Equation is (a) Calculate the gavitational potential point souce with = M 3 (). R µ Rg µ + g µ =GT µ. in the Newtonian
A THEORETICAL ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROSTATIC FILTERS
 PUBLISHING HOUS PROCDINGS OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY, Seies A, OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY Volume 5, Numbe /4, pp.- A THORTICAL ANALYSIS OF TH LCTROSTATIC FILTRS Gleb DRAGAN* Romanian Acaem Calea Victoiei 5, 7 Bucaest,
PUBLISHING HOUS PROCDINGS OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY, Seies A, OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY Volume 5, Numbe /4, pp.- A THORTICAL ANALYSIS OF TH LCTROSTATIC FILTRS Gleb DRAGAN* Romanian Acaem Calea Victoiei 5, 7 Bucaest,
Electric Potential and Gauss s Law, Configuration Energy Challenge Problem Solutions
 Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 5
 ECE 6345 Sping 15 Pof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 5 1 Oveview This set of notes discusses impoved models of the pobe inductance of a coaxially-fed patch (accuate fo thicke substates). A paallel-plate
ECE 6345 Sping 15 Pof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 5 1 Oveview This set of notes discusses impoved models of the pobe inductance of a coaxially-fed patch (accuate fo thicke substates). A paallel-plate
2. Radiation Field Basics I. Specific Intensity
 . Raiation Fiel Basics Rutten:. Basic efinitions of intensity, flux Enegy ensity, aiation pessue E Specific ntensity t Pencil beam of aiation at position, iection n, caying enegy E, pasg though aea, between
. Raiation Fiel Basics Rutten:. Basic efinitions of intensity, flux Enegy ensity, aiation pessue E Specific ntensity t Pencil beam of aiation at position, iection n, caying enegy E, pasg though aea, between
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Review of the H-O model. Problem 1. Assume that the production functions in the standard H-O model are the following:
 Revie of the H-O model Poblem 1 Assume that the poduction functions in the standad H-O model ae the folloing: f 1 L 1 1 ) L 1/ 1 1/ 1 f L ) L 1/3 /3 In addition e assume that the consume pefeences ae given
Revie of the H-O model Poblem 1 Assume that the poduction functions in the standad H-O model ae the folloing: f 1 L 1 1 ) L 1/ 1 1/ 1 f L ) L 1/3 /3 In addition e assume that the consume pefeences ae given
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
$ i. !((( dv vol. Physics 8.02 Quiz One Equations Fall q 1 q 2 r 2 C = 2 C! V 2 = Q 2 2C F = 4!" or. r ˆ = points from source q to observer
 Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
radians). Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 (a) quadrant I angle (b) quadrant II angle is in standard position Terminal side Terminal side Terminal side
 . TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF GENERAL ANGLES In ode to etend the definitions of the si tigonometic functions to geneal angles, we shall make use of the following ideas: In a Catesian coodinate sstem, an
. TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF GENERAL ANGLES In ode to etend the definitions of the si tigonometic functions to geneal angles, we shall make use of the following ideas: In a Catesian coodinate sstem, an
Notes on McCall s Model of Job Search. Timothy J. Kehoe March if job offer has been accepted. b if searching
 Notes on McCall s Model of Job Seach Timothy J Kehoe Mach Fv ( ) pob( v), [, ] Choice: accept age offe o eceive b and seach again next peiod An unemployed oke solves hee max E t t y t y t if job offe has
Notes on McCall s Model of Job Seach Timothy J Kehoe Mach Fv ( ) pob( v), [, ] Choice: accept age offe o eceive b and seach again next peiod An unemployed oke solves hee max E t t y t y t if job offe has
Physics 122, Fall December 2012
 Physics 1, Fall 01 6 Decembe 01 Toay in Physics 1: Examples in eview By class vote: Poblem -40: offcente chage cylines Poblem 8-39: B along axis of spinning, chage isk Poblem 30-74: selfinuctance of a
Physics 1, Fall 01 6 Decembe 01 Toay in Physics 1: Examples in eview By class vote: Poblem -40: offcente chage cylines Poblem 8-39: B along axis of spinning, chage isk Poblem 30-74: selfinuctance of a
CHAPTER 2 DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE. 2.1 Derivation of Machine Equations
 1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
Fields and Waves I Spring 2005 Homework 4. Due 8 March 2005
 Homewok 4 Due 8 Mach 005. Inceasing the Beakdown Voltage: This fist question is a mini design poject. You fist step is to find a commecial cable (coaxial o two wie line) fo which you have the following
Homewok 4 Due 8 Mach 005. Inceasing the Beakdown Voltage: This fist question is a mini design poject. You fist step is to find a commecial cable (coaxial o two wie line) fo which you have the following
Electric Field, Potential Energy, & Voltage
 Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Lecture 2 Date:
 Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
4. Compare the electric force holding the electron in orbit ( r = 0.53
 Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
1 2 U CV. K dq I dt J nqv d J V IR P VI
 o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
2.5 The Quarter-Wave Transformer
 /3/5 _5 The Quate Wave Tansfome /.5 The Quate-Wave Tansfome Reading Assignment: pp. 73-76 By now you ve noticed that a quate-wave length of tansmission line ( λ 4, β π ) appeas often in micowave engineeing
/3/5 _5 The Quate Wave Tansfome /.5 The Quate-Wave Tansfome Reading Assignment: pp. 73-76 By now you ve noticed that a quate-wave length of tansmission line ( λ 4, β π ) appeas often in micowave engineeing
Phys-272 Lecture 18. Mutual Inductance Self-Inductance R-L Circuits
 Phys-7 ectue 8 Mutual nductance Self-nductance - Cicuits Mutual nductance f we have a constant cuent i in coil, a constant magnetic field is ceated and this poduces a constant magnetic flux in coil. Since
Phys-7 ectue 8 Mutual nductance Self-nductance - Cicuits Mutual nductance f we have a constant cuent i in coil, a constant magnetic field is ceated and this poduces a constant magnetic flux in coil. Since
Physics Courseware Physics II Electric Field and Force
 Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
Electric Potential. Outline. Potential Energy per Unit Charge. Potential Difference. Potential Energy Difference. Quiz Thursday on Chapters 23, 24.
 lectic otential Quiz Thusay on Chaptes 3, 4. Outline otential as enegy pe unit chage. Thi fom of Coulomb s Law. elations between fiel an potential. otential negy pe Unit Chage Just as the fiel is efine
lectic otential Quiz Thusay on Chaptes 3, 4. Outline otential as enegy pe unit chage. Thi fom of Coulomb s Law. elations between fiel an potential. otential negy pe Unit Chage Just as the fiel is efine
Transverse Wakefield in a Dielectric Tube with Frequency Dependent Dielectric Constant
 ARDB-378 Bob Siemann & Alex Chao /4/5 Page of 8 Tansvese Wakefield in a Dielectic Tube with Fequency Dependent Dielectic Constant This note is a continuation of ARDB-368 that is now extended to the tansvese
ARDB-378 Bob Siemann & Alex Chao /4/5 Page of 8 Tansvese Wakefield in a Dielectic Tube with Fequency Dependent Dielectic Constant This note is a continuation of ARDB-368 that is now extended to the tansvese
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Eddy Currents and Magnetic Calibrations in LDX using a Copper Plasma. D.P. Boyle, PPPL M.E. Mauel, D.T. Garnier, Columbia J.
 Eddy Cuents and Magneti Calibations in LDX using a Coppe Plasma D.P. Boyle PPPL M.E. Mauel D.T. Ganie Columbia J. Kesne MIT PSFC Coppe Plasma Oveview LDX Magnetis Goals Calibate magneti diagnostis positions
Eddy Cuents and Magneti Calibations in LDX using a Coppe Plasma D.P. Boyle PPPL M.E. Mauel D.T. Ganie Columbia J. Kesne MIT PSFC Coppe Plasma Oveview LDX Magnetis Goals Calibate magneti diagnostis positions
Ion-sound waves (electrostatic low frequency waves)
 OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Jerk and Hyperjerk in a Rotating Frame of Reference
 Jek an Hypejek in a Rotating Fame of Refeence Amelia Caolina Spaavigna Depatment of Applie Science an Technology, Politecnico i Toino, Italy. Abstact: Jek is the eivative of acceleation with espect to
Jek an Hypejek in a Rotating Fame of Refeence Amelia Caolina Spaavigna Depatment of Applie Science an Technology, Politecnico i Toino, Italy. Abstact: Jek is the eivative of acceleation with espect to
Force and Work: Reminder
 Electic Potential Foce and Wok: Reminde Displacement d a: initial point b: final point Reminde fom Mechanics: Foce F if thee is a foce acting on an object (e.g. electic foce), this foce may do some wok
Electic Potential Foce and Wok: Reminde Displacement d a: initial point b: final point Reminde fom Mechanics: Foce F if thee is a foce acting on an object (e.g. electic foce), this foce may do some wok
A Comment on Increasing Returns and Spatial. Unemployment Disparities
 The Society fo conomic Studies The nivesity of Kitakyushu Woking Pape Seies No.06-5 (accepted in Mach, 07) A Comment on Inceasing Retuns and Spatial nemployment Dispaities Jumpei Tanaka ** The nivesity
The Society fo conomic Studies The nivesity of Kitakyushu Woking Pape Seies No.06-5 (accepted in Mach, 07) A Comment on Inceasing Retuns and Spatial nemployment Dispaities Jumpei Tanaka ** The nivesity
Econ 201: Problem Set 2 Answers
 Econ 0: Poblem Set Anses Instucto: Alexande Sollaci T.A.: Ryan Hughes Winte 08 Question (a) The fixed cost is F C = 4 and the total vaiable costs ae T CV (y) = 4y. (b) To anse this question, let x = (x,...,
Econ 0: Poblem Set Anses Instucto: Alexande Sollaci T.A.: Ryan Hughes Winte 08 Question (a) The fixed cost is F C = 4 and the total vaiable costs ae T CV (y) = 4y. (b) To anse this question, let x = (x,...,
Physics 207 Lecture 5. Lecture 5
 Lectue 5 Goals: Addess sstems with multiple acceleations in 2- dimensions (including linea, pojectile and cicula motion) Discen diffeent efeence fames and undestand how the elate to paticle motion in stationa
Lectue 5 Goals: Addess sstems with multiple acceleations in 2- dimensions (including linea, pojectile and cicula motion) Discen diffeent efeence fames and undestand how the elate to paticle motion in stationa
 Basic oces an Keple s Laws 1. Two ientical sphees of gol ae in contact with each othe. The gavitational foce of attaction between them is Diectly popotional to the squae of thei aius ) Diectly popotional
Basic oces an Keple s Laws 1. Two ientical sphees of gol ae in contact with each othe. The gavitational foce of attaction between them is Diectly popotional to the squae of thei aius ) Diectly popotional
Chapter 15 VECTORS EXERCISE 15A. Scale: 1 cm 10 km h 1 1 cm 10 ms 1 N. 35 ms km h-1 W S. Scale: N cm 10 m. 60 ms -1.
 Chate VECTORS EXERCISE a Sale: Sale: m 0 km h m 0 ms W E ms - 0 km h- S W S E W 0 0 E Sale: m 0 m 60 ms - m unway S Sale: m 0 ms a Sale: m newtons Sale: m newtons 7 newtons W S E 60 newtons W S E a Sale:
Chate VECTORS EXERCISE a Sale: Sale: m 0 km h m 0 ms W E ms - 0 km h- S W S E W 0 0 E Sale: m 0 m 60 ms - m unway S Sale: m 0 ms a Sale: m newtons Sale: m newtons 7 newtons W S E 60 newtons W S E a Sale:
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department. Problem Set 10 Solutions. r s
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
Properties of the natural logarithm and exponential functions
 Poeties of the natual logaithm an eonential functions Define fo ositive the function A() as the aea fom to une the hyeolay Since thee is no with, A() 0 By efinition the eivative of A() is given y the limit
Poeties of the natual logaithm an eonential functions Define fo ositive the function A() as the aea fom to une the hyeolay Since thee is no with, A() 0 By efinition the eivative of A() is given y the limit
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Solutions to Problems : Chapter 19 Problems appeared on the end of chapter 19 of the Textbook
 Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Spring 2005
 MIT OpenouseWae http://ocw.mit.edu 6.641 Electomagnetic Fields, Foces, and Motion Sping 2005 Fo infomation about citing these mateials o ou Tems of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/tems. 6.641 Electomagnetic
MIT OpenouseWae http://ocw.mit.edu 6.641 Electomagnetic Fields, Foces, and Motion Sping 2005 Fo infomation about citing these mateials o ou Tems of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/tems. 6.641 Electomagnetic
Transfer Matrix Method
 9/6/17 Instucto D. Ramond Rumpf (915) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.edu 5337 Computational lectomagnetics Lectue #4 Tansfe Mati Method Lectue 4These notes ma contain copighted mateial obtained unde fai use ules.
9/6/17 Instucto D. Ramond Rumpf (915) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.edu 5337 Computational lectomagnetics Lectue #4 Tansfe Mati Method Lectue 4These notes ma contain copighted mateial obtained unde fai use ules.
Conventional Paper-I (a) Explain the concept of gradient. Determine the gradient of the given field: ( )
 EE-Conventional Pape-I IES-013 www.gatefoum.com Conventional Pape-I-013 1. (a) Eplain the concept of gadient. Detemine the gadient of the given field: V ρzsin φ+ z cos φ+ρ What is polaization? In a dielectic
EE-Conventional Pape-I IES-013 www.gatefoum.com Conventional Pape-I-013 1. (a) Eplain the concept of gadient. Detemine the gadient of the given field: V ρzsin φ+ z cos φ+ρ What is polaization? In a dielectic
Then the number of elements of S of weight n is exactly the number of compositions of n into k parts.
 Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Geneating Function In a geneal combinatoial poblem, we have a univee S of object, and we want to count the numbe of object with a cetain popety. Fo example, if S i the et of all gaph, we might want to
Transmission Line Analysis of Beam Deflection in a BPM Stripline Kicker
 UCR-JC-126073 PREPRINT Tansmission ine Analysis of Beam Defletion in a BPM Stipline Kike Geoge J. Capoaso Yu Ju Chen Bian Poole This pape was pepaed fo submittal to the 1997 Patile Aeleato Confeene Vanouve,
UCR-JC-126073 PREPRINT Tansmission ine Analysis of Beam Defletion in a BPM Stipline Kike Geoge J. Capoaso Yu Ju Chen Bian Poole This pape was pepaed fo submittal to the 1997 Patile Aeleato Confeene Vanouve,
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) ,
 R Pena Towe, Road No, Contactos Aea, Bistupu, Jamshedpu 8, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com IIT JEE Mathematics Pape II PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION I Single Coect Answe Type This section contains 8 multiple
R Pena Towe, Road No, Contactos Aea, Bistupu, Jamshedpu 8, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com IIT JEE Mathematics Pape II PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION I Single Coect Answe Type This section contains 8 multiple
σ = neμ = v D = E H, the Hall Field B Z E Y = ee y Determining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x I, J x E y B z F = qe + qv B F y
 Detemining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x + + + + + + + + + + + --------- E y I, J x F = qe + qv B F y = ev D B z F y = ee y B z In steady state, E Y = v D B Z = E H, the Hall Field Since v D =-J x
Detemining n and μ: The Hall Effect V x, E x + + + + + + + + + + + --------- E y I, J x F = qe + qv B F y = ev D B z F y = ee y B z In steady state, E Y = v D B Z = E H, the Hall Field Since v D =-J x
Reflectance spectra for Si
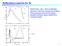 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Section 5: Magnetostatics
 ection 5: Magnetostatics In electostatics, electic fiels constant in time ae pouce by stationay chages. In magnetostatics magnetic fiels constant in time ae pouces by steay cuents. Electic cuents The electic
ection 5: Magnetostatics In electostatics, electic fiels constant in time ae pouce by stationay chages. In magnetostatics magnetic fiels constant in time ae pouces by steay cuents. Electic cuents The electic
Classical Approach to the Theory of Elementary Particles
 Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Matthias Liepe, P4456/7656, Spring 2010, Cornell University Slide 1. Matthias Liepe, P4456/7656, Spring 2010, Cornell University Slide 2
 5. F ystems ad Patile Aeleatio 5. Waveguides 5..3 Cylidial Waveguides 5. Aeleatig F Cavities 5.. Itodutio 5.. Tavelig wave avity: dis loaded waveguide 5..3 tadig wave avities 5..4 Highe-Ode-Modes 5..5
5. F ystems ad Patile Aeleatio 5. Waveguides 5..3 Cylidial Waveguides 5. Aeleatig F Cavities 5.. Itodutio 5.. Tavelig wave avity: dis loaded waveguide 5..3 tadig wave avities 5..4 Highe-Ode-Modes 5..5
Gravitoelectromagnetism. II. Speed of Light in Gravitational Field
 Zbigniew Osiak aitoeletomagnetism. II. May 9, 8 aitoeletomagnetism. II. peed of Light in aitational Field Zbigniew Osiak E-mail: zbigniew.osiak@gmail.om http://oid.og/--57-36x http://ixa.og/autho/zbigniew_osiak
Zbigniew Osiak aitoeletomagnetism. II. May 9, 8 aitoeletomagnetism. II. peed of Light in aitational Field Zbigniew Osiak E-mail: zbigniew.osiak@gmail.om http://oid.og/--57-36x http://ixa.og/autho/zbigniew_osiak
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
Phys 1215, First Test. September 20, minutes Name:
 Phys 115, Fist Test. Septembe 0, 011 50 minutes Name: Show all wok fo maximum cedit. Each poblem is woth 10 points. k =.0 x 10 N m / C ε 0 = 8.85 x 10-1 C / N m e = 1.60 x 10-1 C ρ = 1.68 x 10-8 Ω m fo
Phys 115, Fist Test. Septembe 0, 011 50 minutes Name: Show all wok fo maximum cedit. Each poblem is woth 10 points. k =.0 x 10 N m / C ε 0 = 8.85 x 10-1 C / N m e = 1.60 x 10-1 C ρ = 1.68 x 10-8 Ω m fo
Physics 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #15
 Physics 7 HOMEWORK SSIGNMENT #5 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th eition Chapte 8: Poblem 4 Chapte 9: Poblems,, 5, 54 **4 small plastic with a mass of 6.5 x - kg an with a chage of.5 µc is suspene fom an insulating
Physics 7 HOMEWORK SSIGNMENT #5 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th eition Chapte 8: Poblem 4 Chapte 9: Poblems,, 5, 54 **4 small plastic with a mass of 6.5 x - kg an with a chage of.5 µc is suspene fom an insulating
Supplementary Figure 1. Circular parallel lamellae grain size as a function of annealing time at 250 C. Error bars represent the 2σ uncertainty in
 Supplementay Figue 1. Cicula paallel lamellae gain size as a function of annealing time at 50 C. Eo bas epesent the σ uncetainty in the measued adii based on image pixilation and analysis uncetainty contibutions
Supplementay Figue 1. Cicula paallel lamellae gain size as a function of annealing time at 50 C. Eo bas epesent the σ uncetainty in the measued adii based on image pixilation and analysis uncetainty contibutions
How to Obtain Desirable Transfer Functions in MIMO Systems Under Internal Stability Using Open and Closed Loop Control
 How to Obtain Desiable ansfe Functions in MIMO Sstems Unde Intenal Stabilit Using Open and losed Loop ontol echnical Repot of the ISIS Goup at the Univesit of Note Dame ISIS-03-006 June, 03 Panos J. Antsaklis
How to Obtain Desiable ansfe Functions in MIMO Sstems Unde Intenal Stabilit Using Open and losed Loop ontol echnical Repot of the ISIS Goup at the Univesit of Note Dame ISIS-03-006 June, 03 Panos J. Antsaklis
Homework Set 3 Physics 319 Classical Mechanics
 Homewok Set 3 Phsics 319 lassical Mechanics Poblem 5.13 a) To fin the equilibium position (whee thee is no foce) set the eivative of the potential to zeo U 1 R U0 R U 0 at R R b) If R is much smalle than
Homewok Set 3 Phsics 319 lassical Mechanics Poblem 5.13 a) To fin the equilibium position (whee thee is no foce) set the eivative of the potential to zeo U 1 R U0 R U 0 at R R b) If R is much smalle than
rect_patch_cavity.doc Page 1 of 12 Microstrip Antennas- Rectangular Patch Chapter 14 in Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design (4th Edition) by Balanis
 ect_patch_cavit.doc Page 1 of 1 Micostip Antennas- Rectangula Patch Chapte 14 in Antenna Theo, Analsis and Design (4th dition) b Balanis Cavit model Micostip antennas esemble dielectic-loaded cavities
ect_patch_cavit.doc Page 1 of 1 Micostip Antennas- Rectangula Patch Chapte 14 in Antenna Theo, Analsis and Design (4th dition) b Balanis Cavit model Micostip antennas esemble dielectic-loaded cavities
A moving charged particle creates a magnetic field vector at every point in space except at its position.
 1 Pat 3: Magnetic Foce 3.1: Magnetic Foce & Field A. Chaged Paticles A moving chaged paticle ceates a magnetic field vecto at evey point in space ecept at its position. Symbol fo Magnetic Field mks units
1 Pat 3: Magnetic Foce 3.1: Magnetic Foce & Field A. Chaged Paticles A moving chaged paticle ceates a magnetic field vecto at evey point in space ecept at its position. Symbol fo Magnetic Field mks units
The Stability of Wave-like Pulsar Winds
 The Stailit of Waelike Pulsa Wins Paul Withes, supeise Ane Melatos at the Califonia Institute of Tehnolog Eept hee speifi efeene is mae to the ok of othes, this ok is oiginal an has not een sumitte eithe
The Stailit of Waelike Pulsa Wins Paul Withes, supeise Ane Melatos at the Califonia Institute of Tehnolog Eept hee speifi efeene is mae to the ok of othes, this ok is oiginal an has not een sumitte eithe
of Technology: MIT OpenCourseWare). (accessed MM DD, YYYY). License: Creative Commons Attribution- Noncommercial-Share Alike.
 MIT OpenCouseWae http://ocw.mit.eu 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics an Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation fomat: Makus Zahn, Eich Ippen, an Davi Staelin, 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics
MIT OpenCouseWae http://ocw.mit.eu 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics an Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation fomat: Makus Zahn, Eich Ippen, an Davi Staelin, 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematical Model of Dust Whirl
 Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 2 Autumn 2012
 763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 2 Autumn 2012 1. Continuous Random Walk Conside a continuous one-dimensional andom walk. Let w(s i ds i be the pobability that the length of the i th displacement
763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 2 Autumn 2012 1. Continuous Random Walk Conside a continuous one-dimensional andom walk. Let w(s i ds i be the pobability that the length of the i th displacement
